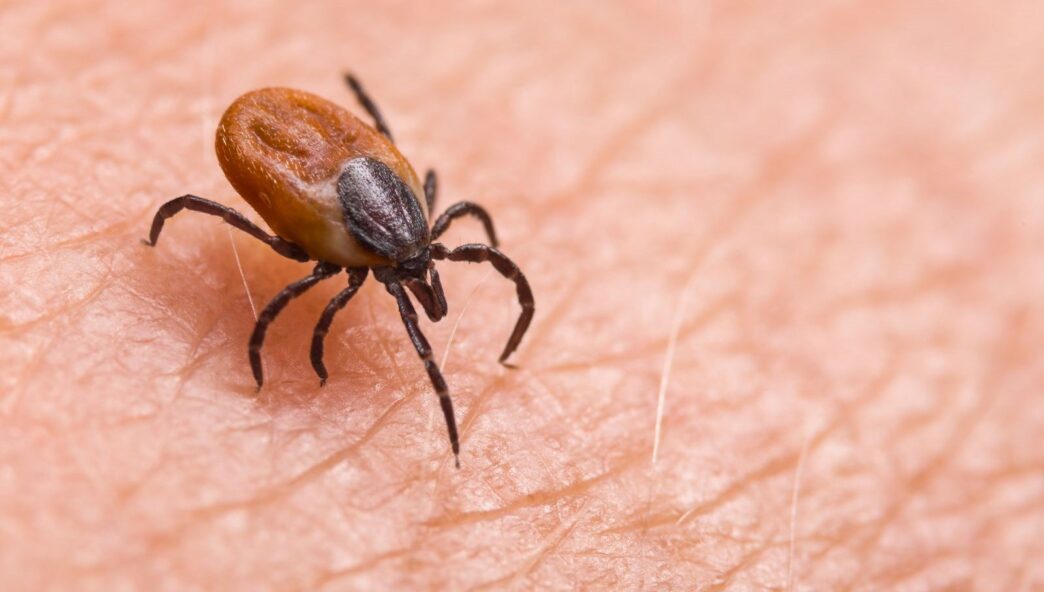
Ticks are becoming a greater threat due to global warming as they travel between continents and carry the diseases they carry to new regions thanks to migratory birds. Experts stated that there is a risk of rapid spread of tick-borne diseases.
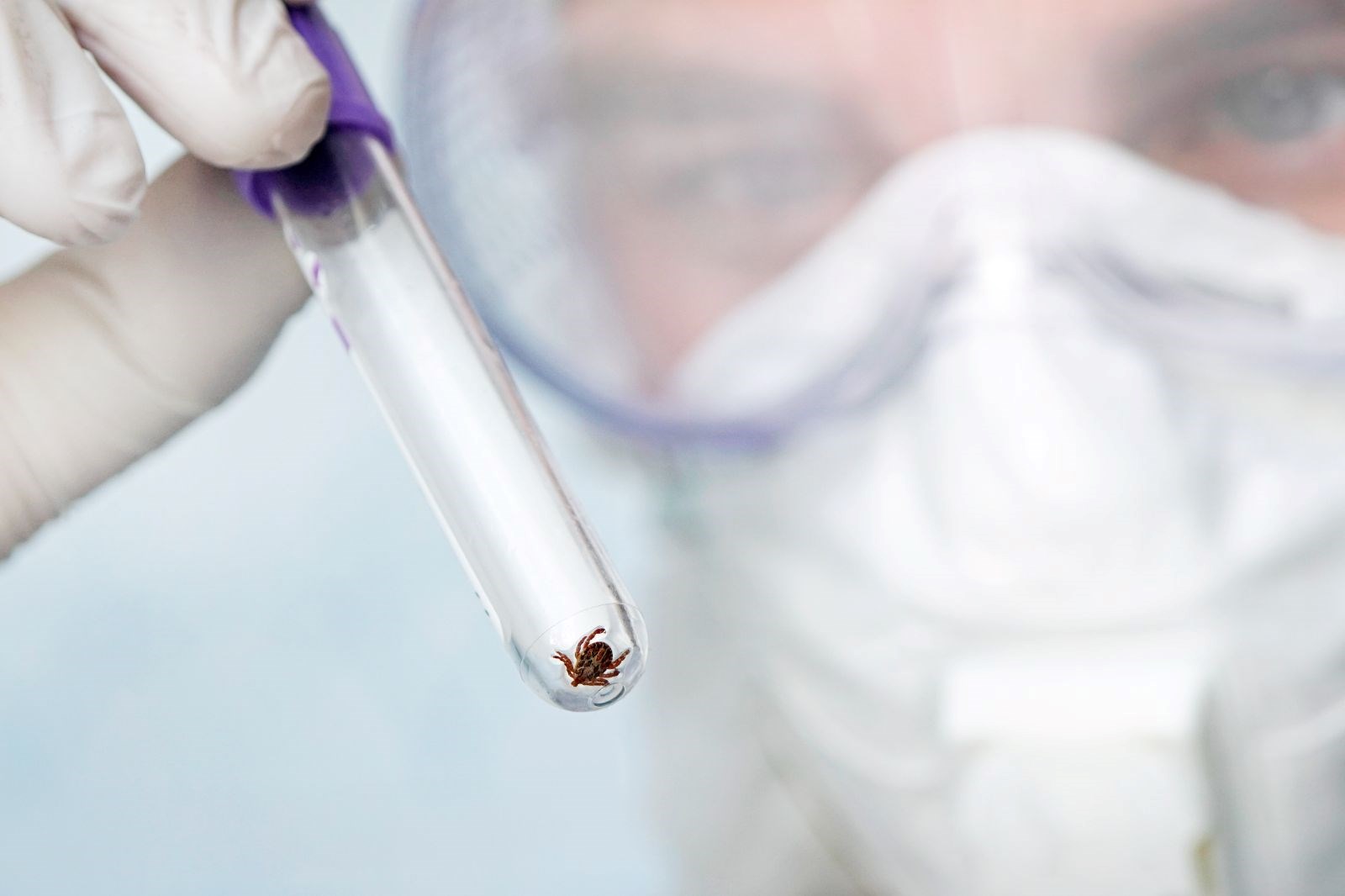
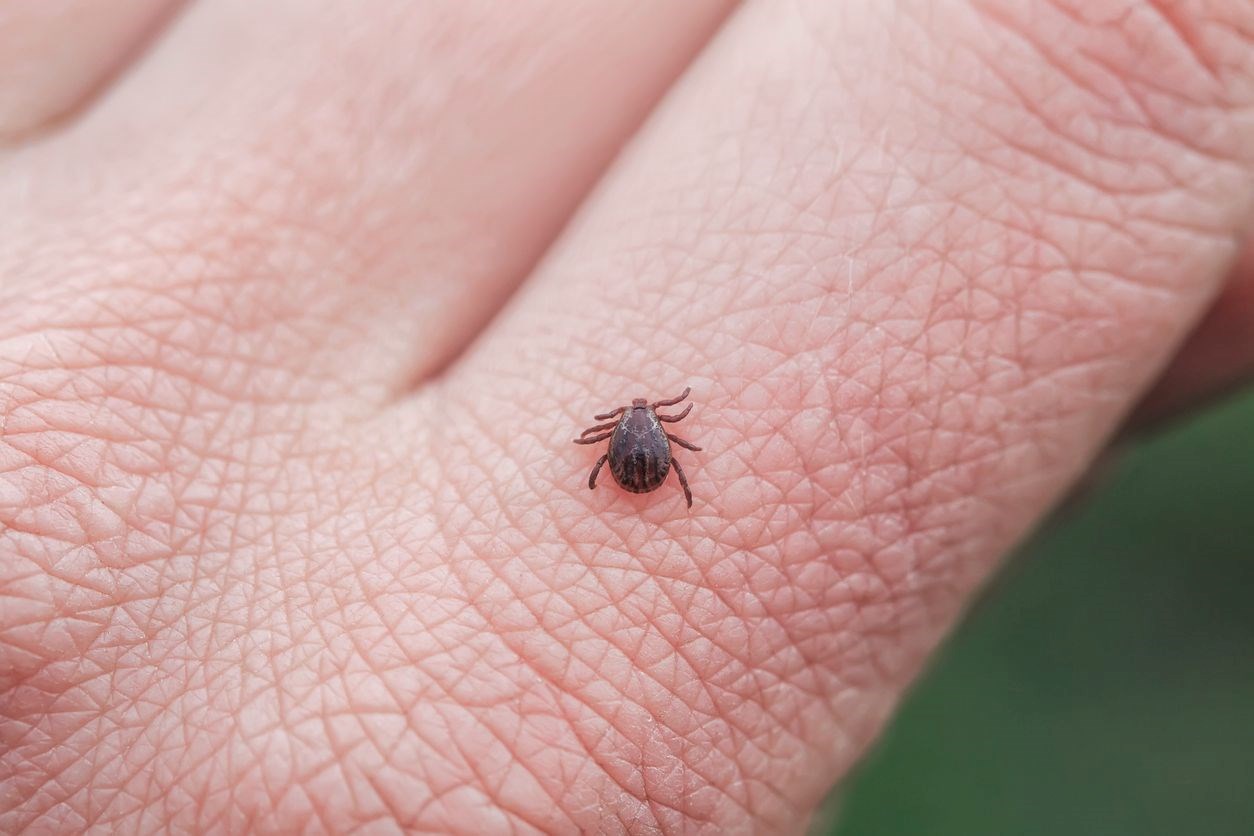


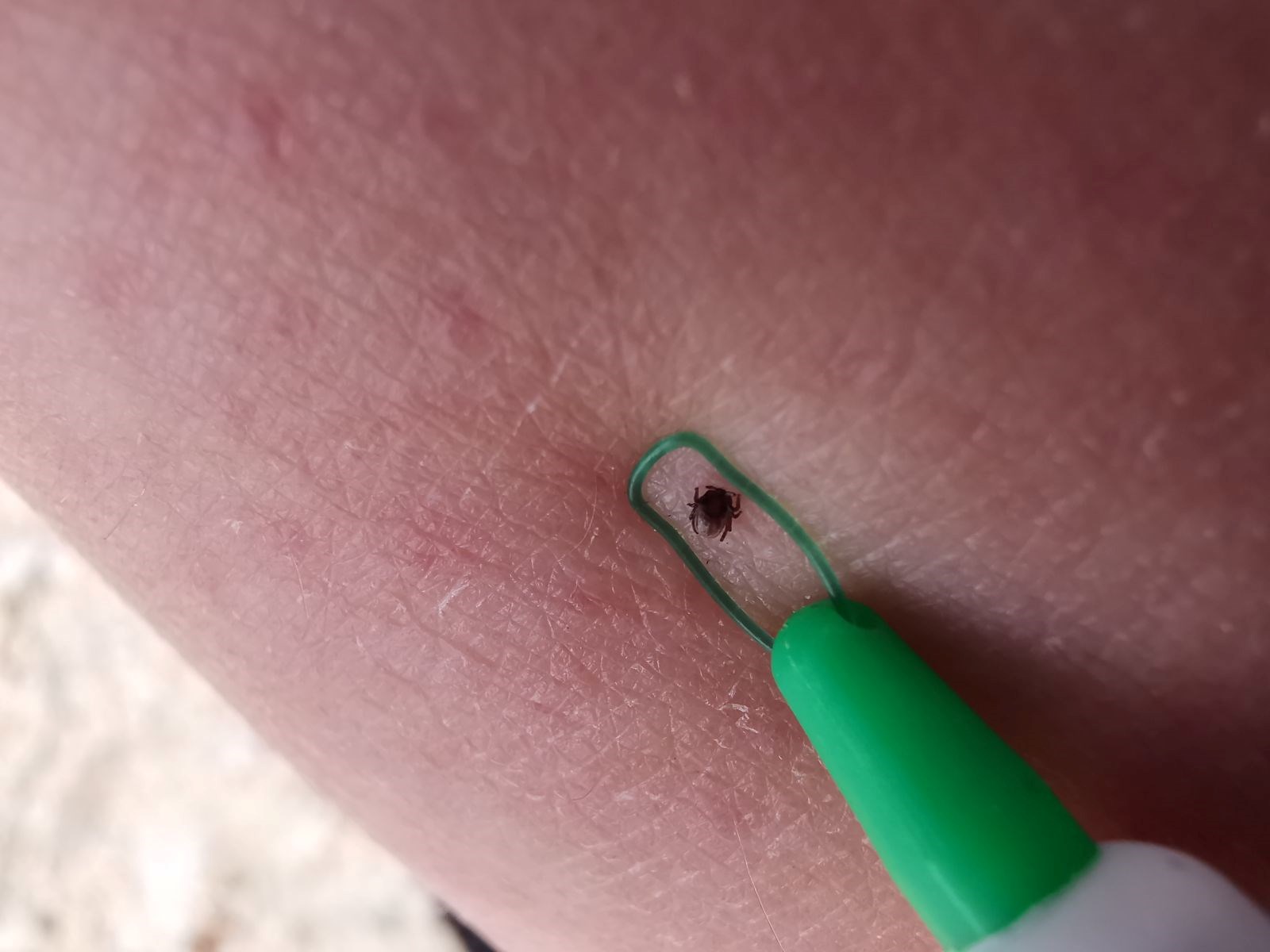


This tick crisis, which is increasing with the effect of global warming, is leading health authorities and scientists to take new precautions. The borderless nature of diseases carried by ticks poses a great threat to both health and environmental safety.













